CVSS is short for Common Vulnerability Scoring System and is according to Wikipedia a technical standard for assessing the severity of vulnerabilities in computing systems.
Typically you use an online CVSS calculator, click a few checkboxes and radio buttons and then you magically get a number from 0 to 10. There are also different versions of CVSS.
Every CVE filed to MITRE is supposed to have a CVSS score set. CVEs that are registered that lack this information will get “amended” by an ADP (Authorized Data Publishers) that think of it as their job. In the past NVD did this. Nowadays CISA does it. More on this below.
Problems
Let’s say you write a tool and library that make internet transfers. They are used literally everywhere, in countless environments and with an almost impossible number of different build combinations, target operating systems and CPU architectures. Let’s call it curl.
When you find a theoretical security problem in this product (theoretical because most problems are never actually spotted exploited), how severe is it? The CVSS calculation has a limited set of input factors that tend to result in a fairly high number for a network product. What if we can guess that the problem is only used by a few or only affects an unusual platform? Not included.
The CVSS scoring is really designed for when you know exactly when and how the product is used and how an exploit of the flaw affects it. Then it might at least work. For a generic code base shipped in a tarball that runs in more than twenty billion installations it does less so.
If you look around you can easily find numerous other (and longer) writings about the problems and challenges with CVSS. We are not alone thinking this.
CVSS is used
At the same time, it seems the popularity of security scanners have increased significantly over the last few years. The kind of products that scan your systems checking for vulnerable products and show you big alerts and warnings when they do.
The kind of programs that looks for a product, figures out a version number and then shouts if it finds a registered CVE for that product and version with a CVSS score above a certain threshold.
This kind of product that indirectly tricks users to deleting operating system components to silence these alerts. We even hear of people who have contractual agreements that say they must address these alerts within N number of business days or face consequences.
Just days ago I was contacted by users on macOS who were concerned about a curl CVE that their scanner found in the libcurl version shipped by Apple. Was their tool right or wrong? Do you think anyone involved in that process actually can tell? Do you think Apple cares?
curl skips CVSS
In the curl project we have given up trying to use CVSS to get a severity score and associated severity level.
In the curl security team we instead work hard to put all our knowledge together and give a rough indication about the severity by dividing it into one out of four levels: low, medium, high, critical.
We believe that because we are not tied to any (flawed and limited) calculator and because we are intimately familiar with the code base and how it is used, we can assess and set a better security severity this way. It serves our users better.
Part of our reason to still use these four levels is that our bug-bounty‘s reward levels are based on the level.
As a comparison, The Linux kernel does not even provide that course-grained indication, based on similar reasoning to why we don’t provide the numeric scores.
This is not treated well
The curl project is a CNA, which means that we reserve and publish our own CVE Ids to the CVE database. There is no middle man interfering and in fact no one else can file curl CVE entries anymore without our knowledge and us having a saying about it. That’s good.
However, the CVE system itself it built on the idea that every flaw has a CVSS score. When someone like us creates CVE entries without scores, that leaves something that apparently is considered a gaping sore in the system that someone needs to “fix”.
Who would “fix” this?
Authorized Data Publishers
A while ago this new role was added to the CVE ecosystem called ADPs. This job was previously done a little on the side but roughly the same way by NVD who would get all the CVEs, edit them and then publish them all themselves to the world with their additions. And the world really liked that and used the NVD database.
However NVD kind of drowned themselves by this overwhelming work and it has instead been replaced by CISA who is an “ADP” and is thus allowed to enrich CVE entries in the database that they think need “improvement”.
The main thing they seem to detect and help “fix” is the lack of CVSS in published CVE entries. Like every single curl CVE because we don’t participate in the CVSS dance.
No clues but it must get a score
Exactly in the same way this system was broken before when NVD did it, this new system is broken when CISA does it.
I don’t have the numbers for exactly how many CVE entries they do this “enrichment” for (there were over 40,000 CVEs last year but a certain amount of them had CVSS filed in by their CNAs). I think it is safe to assume that the volume is high and since they are filed for products in all sorts of categories it is certainly impossible for CISA to have experts in the many products and technologies each CVE describes and affects.
So: given limited time and having no real clue what the issues are about, the individuals in this team click some buttons in a CVSS calculator, get a score, a severity and then (presumably) quickly move on the next issue. And the next. And the next. In a never-ending stream of incoming security issues.
How on earth does anyone expect them to get this right? I mean sure, in some or perhaps even many cases they might get close because of luck, skill or something but the system is certainly built in a way that just screams: this will end up crazy wrong ever so often.
A recent example
In the end of 2024 I was informed by friends that several infosec related websites posted about a new curl-related critical security problem. Since we have not announced any critical security problems since 2013, that of course piqued my interest so I had a look.
It turned out that CISA had decided that CVE-2024-11053 should be earned a CVSS 9.1 score: CRITICAL, and now scanners and news outlets had figured that out. Or would very soon.
The curl security team had set the severity to LOW because of the low risk and special set of circumstances that are a precondition for the problem. Go read it yourself – the fine thing with CVEs for Open Source products is that the source, the fix and everything is there to read and inspect as much as we like.
The team of actual experts who knows this code and perfectly understands the security problem says LOW. The team at CISA overrides that and insists that are all wrong and that this problem risks breaking the Internet. Because we apparently need a CVSS at all costs.
A git repository
One positive change that the switch to CISA from NVD brought is that now they host their additional data in GitHub repository. Once I was made aware of this insane 9.1 score, I took time of my Sunday afternoon with my family and made a pull-request there urging them to at least lower the score to 5.3. That was a score I could get the calculator to tell me.
I wanted to have this issue sorted and stomped down as quickly as possible to if possible reduce the risk that security scanners everywhere would soon start alerting on this and we would get overloaded with queries from concerned and worried users.
It’s not like CISA gets overloaded by worried users when they do this. Their incompetence here puts a load on no one else but the curl project. But sure, they got their CVSS added.
After my pull request it took less than ninety minutes for them to update the curl records. Without explanation, with no reference to my PR, they now apparently consider the issue to be CVSS 3.4.
I’m of course glad it is no longer marked critical. I think you all understand exactly how arbitrary and random this scoring approach is.
A problem with the initial bad score getting published is of course that a certain number of websites and systems are really slow or otherwise bad at updating that information after they initially learned about the critical score. There will linger websites out there speaking about this “critical” curl bug for a long time now. Thanks CISA!
Can we avoid this?
In the curl security team we have discussed setting “fixed” (fake) scores on our CVE entries just in order to prevent CISA or anyone else to ruin them, but we have decided not to since that would be close to lying about them and we actually work fiercely to make sure we have everything correct and meticulously described.
So no, since we do not do the CVSS dance, we unfortunately will continue having CISA do this to us.
Stop mandatory CVSS?
I am of course advocating strongly within the CNA ecosystem that we should be able to stop CISA from doing this, but I am just a small cog in a very large machine. A large machine that seems to love CVSS. I do not expect to have much success in this area anytime soon.
And no, I don’t think switching to CVSS 4.0 or updates to this system is ultimately going to help us. The problem is grounded in the fact that a single one-dimensional score is just too limited. Every user or distributor of the project should set scores for their different use cases. Maybe even different ones for different cases. Then it could perhaps work.
But I’m not in this game for any quick wins. I’m on the barricades for better (Open Source) security information, and to stop security misinformation. Ideally for the wider ecosystem, because I think we are far from alone in this situation.
The love of CVSS is strong and there is a lot of money involved based on and relying on this.
Minor update
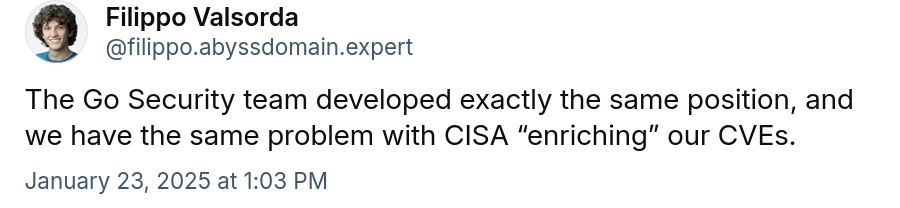
After posting this, I got confirmation that the Go Security team does what we do and has the same problems. Filippo Valsorda told me on Bluesky. Just to show that this is a common pattern.
Update two
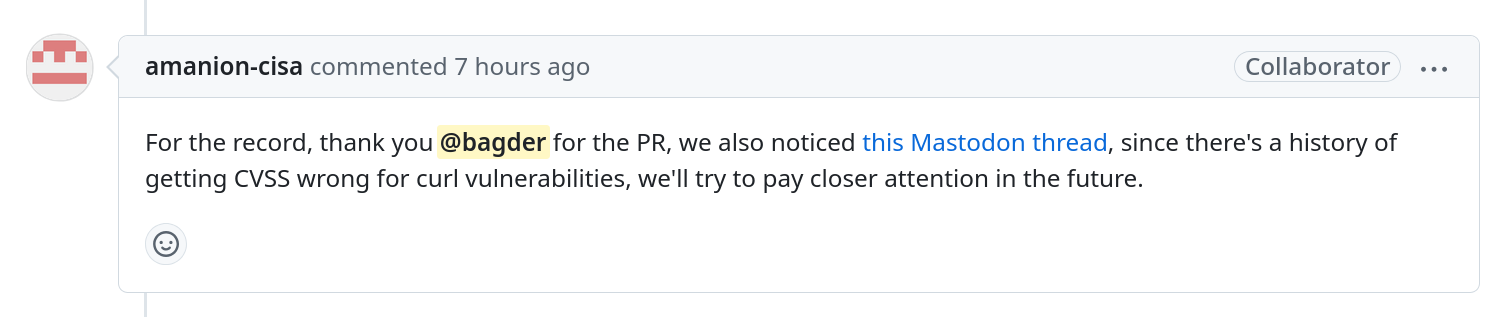
Some fourteen hours after I posted this blog post and it spread around the world, my enrichment PR to CISA I mentioned above got this added comment:
While it is good to be recognized, it does not feel like it will actually address the underlying problem here.
Update three
What feels like two hundred persons have pointed out that the CVSS field is not mandatory in the CVE records. It is a clarification that does not add much. The reality is that users seem to want the scores so bad that CISA will add CVSS nonetheless, mandatory or not.