Welcome to this new curl release!
Release video
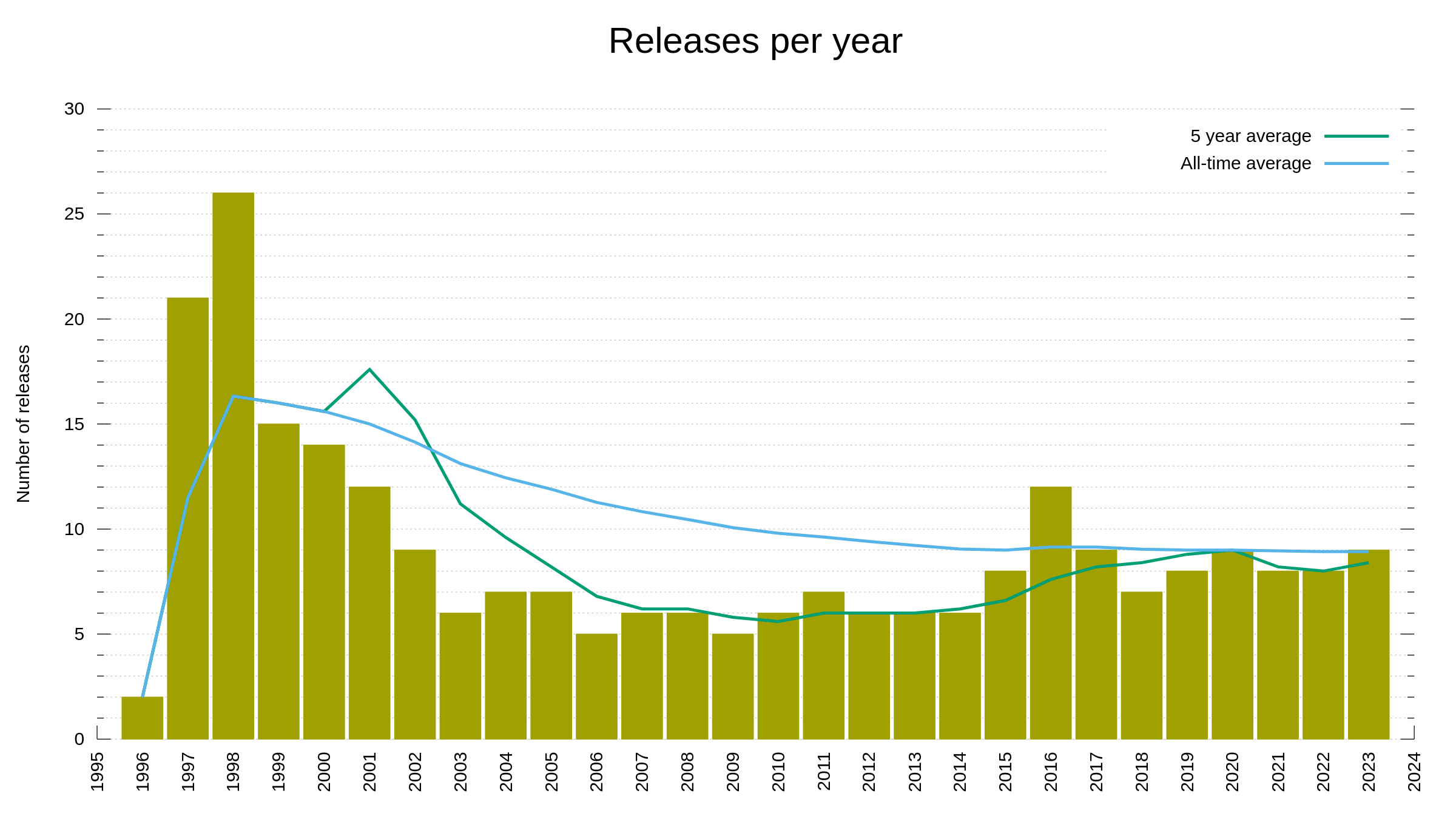
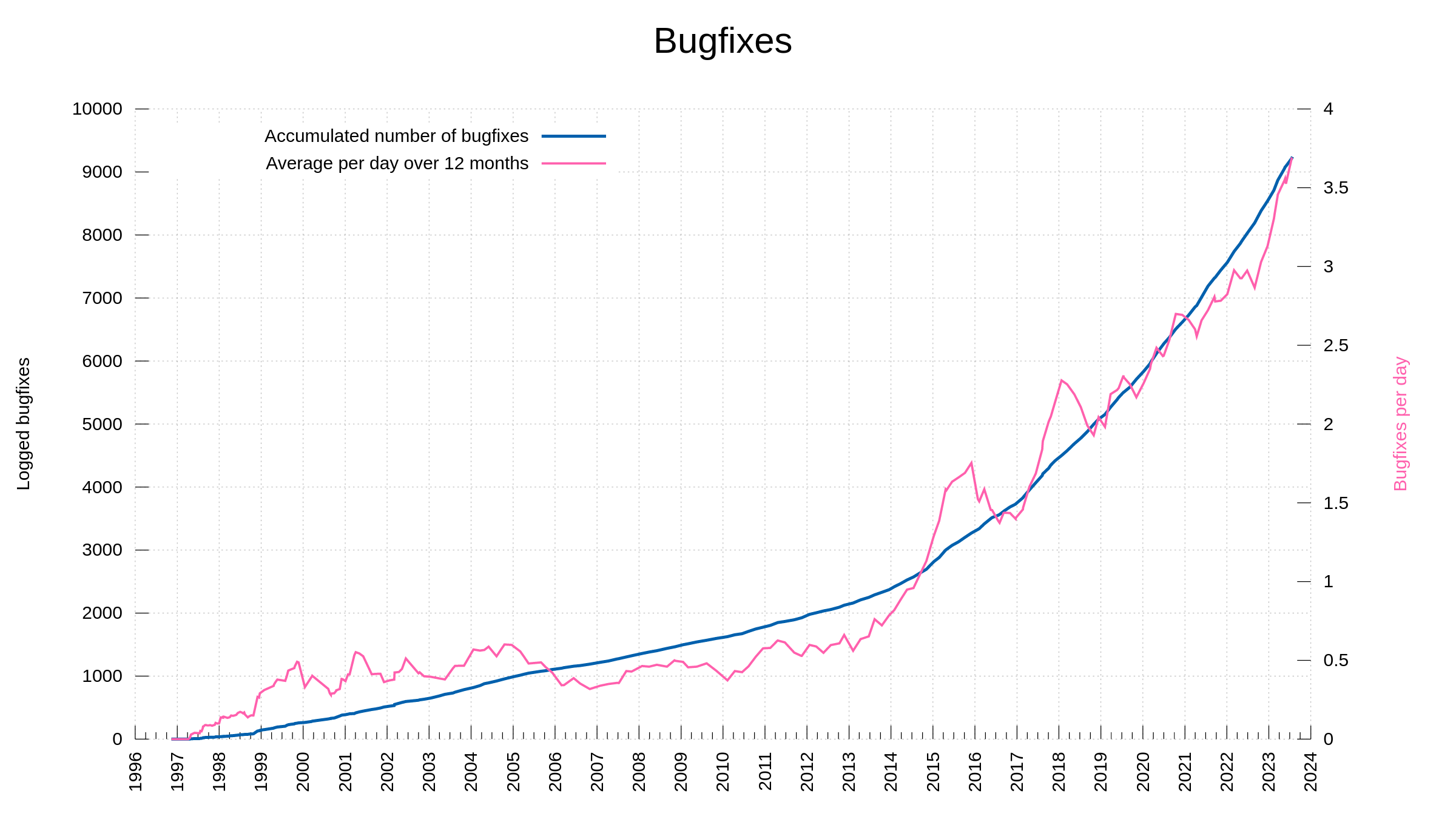
Numbers
the 251st release
9 changes
49 days (total: 9,308)
174 bug-fixes (total: 9,415)
296 commits (total: 30,942)
1 new public libcurl function (total: 92)
0 new curl_easy_setopt() option (total: 303)
2 new curl command line option (total: 257)
80 contributors, 50 new (total: 2,977)
40 authors, 20 new (total: 1,193)
1 security fix (total: 146)
Numbers notes:
- the release counter now also includes project releases done before the name was changed to curl.
- The number of security fixes is adjusted due to the recently rejected CVE-2023-32001
Security
We publish a security advisory in association with today’s release.
HTTP headers eat all memory
[CVE-2023-38039] When curl retrieves an HTTP response, it stores the incoming headers so that they can be accessed later via the libcurl headers API.
However, curl did not have a limit in how many or how large headers it would accept in a response, allowing a malicious server to stream an endless series of headers and eventually cause curl to run out of heap memory.
Changes
curl: make %output{} in -w specify a file to write to
The super handy option –write-out become even more convenient now as it can redirect its output into a specific file and not just stdout and stderr.
curl: add “variable” support
The new variable concept now only lets users use environment variables on config files but also opens up for new ways to use curl command lines effectively.
remove gskit support
The gskit TLS library is no longer a provided option when building curl.
remove NSS support
The NSS TLS library is no longer a provided option when building curl. curl still supports building with twelve different TLS libraries even after the removal of these two.
configure –disable-bindlocal builds curl without local binding support
As a next step in the gradual movement to allow more and more features to get enabled/disabled at build time, the time came to the bindlocal function, which is the feature that binds the local end of a connection. Primarily intended for tiny-curl purposes when you aim for a minimal footprint build.
make tracing available in non-debug builds
Starting now, libcurl offers curl_global_trace and curl offers –trace-config to ask for what specific details to include in the verbose logging output. This is a way for a non-debug build to provide more protocol level details from transfers in ways that were previously not possible. Allows for users to report bugs better and provide more insights from real-world problematic scenarios.
CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS defaults to 30
As a precaution, we change the default from unlimited to 30.
CURLU_PUNY2IDN – convert punycode to IDN
The URL API gets the ability to convert to an International Domain Name when given a punycode version. Previously it could only do the conversion in the other direction.
wolfssl: support loading system CA certificates
curl built with wolfSSL now can use the “native CA” option which then makes it possible to use the native CA store on several platforms instead of using a separately provided external file.
Bugfixes
More than 160 bugfixes are logged for this release, but here are a few selected highlights.
accept and parse IPv6 addresses in alt-svc response headers
Previously curl would not parse and accept such hosts.
c-ares: reduce timeout to 2000ms
The default c-ares DNS timeout is set to the same time that c-ares itself has changed to in their next pending release.
make CURLOPT_HAPROXY_CLIENT_IP set the source IP
It was wrongly set as destination instead of source.
cmake: ten separate improvements
Numerous smaller and larger fixes that made the cmake build of curl several notches better.
stop halving the remaining connect timeout when less than 600 ms left
When curl connects to a host that resolves to multiple IP addresses, it allows half the timeout time for the current IP before it moves on to attempt the next IP in the list. That “halving” is now stopped when there is less than 600 milliseconds left to reduce problems with too short times.
docs: rewrite to present tense
Most of the curl documentation now says “this option does this” instead of “this option will do this”
escape all dashes (ASCII minus) to avoid Unicode hyphens in curl.1 man page
It turns out the curl man page as generated previously, would make the man command use a Unicode hyphen instead of ASCII minus when displayed. This broke copy and paste and it made it impossible to properly search for minus/dash when viewing the man page.
accept leading whitespace on first HTTP response header
curl is now less strict if the first HTTP/1 response header starts with space or tab, thus looking like it is a “fold” when it not. Other commonly used tools/browsers accept this kind of bad syntax and so does curl now.
avoid too early HTTP/2 connection re-use/multiplexing
When doing lots of parallel transfers curl might need to create a second connection when the first reaches its maximum number of streams. In that situation, curl would try to multiplex on that new connection too early, already before it was properly setup and be ready for use, leading to transfer errors.
http/http2/http3: fix sending large requests
Logic for all supported HTTP versions had (different) issues in handling sending very large requests.
aws-sigv4: canonicalize the query
Using aws-sigv4 authentication would fail if the query part was not manually crafted to be correct: sorted, uppercase %-encoding and all the name/value pairs alpha-sorted. Now curl does this itself.
make aws-sigv4 not require TLS to be used
The –aws-sigv4 option no longer requires an HTTPS:// URL to be used.
lib: move mimepost data from ->req.p.http to ->state
The moving of internal data from one struct to another made data survive between two requests and thus fixed a bug involving redirects with MIMEPOST that needed to rewind.
use PF_INET6 family lookups when CURL_IPRESOLVE_V6 is set
Turns out curl would still resolve both IPv4 and IPv6 names even if ipv6-only connections were being requested, thus getting some extra names in vein.
system.h: add CURL_OFF_T definitions on HP-UX with HP aCC
Starting now, curl builds properly on more HP-UX machines.
tests: update cookie expiry dates to far in the future
curl’s test suite now runs fine even when executed in a year after 2038.
tool_filetime: make -z work with file dates before 1970
The -z option can get the file date off a local file and use that in a HTTP time condition request, but if the file was older than January 1 1970 it would act wrongly.
transfer: also stop the sending on closed connection
When curl sent off a HTTP/1 request and the connection was closed before the sending was complete, curl could end up not detecting that and ending the transfer correctly.
don’t set TIMER_STARTTRANSFER on first send
Adjustments were made to make this timestamp work as actually documented.
make zoneid duplicated in curl_url_dup
This dup function did not correctly duplicate the zone id from the source handle, making it an incomplete duplicate.
quic: don’t set SNI if hostname is an IP address
curl would wrongly populate the SNI field with the IP address when doing QUIC connections to such.
Next
This is a dot-zero release. If there are any important enough regressions shipped in this version, we will do a follow-up release within shortly. Report all and any problems you spot.